Concrete vs Timber Floors There are 2 types of floor construction used in the building industry today;The existing concrete floor can be used as a base, however a new damp proof membrane (DPM) will need to be introduced DPMs come in solid or liquid form, the latter being a practicable solution for a garage conversion Manufacturers will be able to advise A suitable gauge damp proof membrane (DPM) and thermal insulation must be providedDamp proof membrane (DPM) On suspended timber floors the floor construction occurs, the insulation should be cut back and a timber batten of the same thickness as the insulation inserted to reinforce the edge Where acoustic insulation is required, the batten thickness
Q Tbn And9gcsoo00pmp Jo39lntwqiman Kyqnkiizr2egma 29un93tjzu39 Usqp Cau
Dpm suspended timber floor insulation
Dpm suspended timber floor insulation-Underfloor thermal insulation of suspended timber floors involves removing the existing pine floorboards or any other type of boarding This to eliminate the empty spaces between the joists that allow the cold draughts to reach the subfloor A galvanised mesh bed is fixed between the joists to properly hold in place the insulation • Timber floor boards eg tongue–and–groove 18 mm thick plywood, should then be laid over the insulation and battens with staggered cross–joints in accordance with DD ENV 00 • An expansion gap of 2 mm per metre run of floor, or a minimum of 10 mm overall, whichever is the greater, should be provided between the floor boards and the perimeter walls



Www Premierguarantee Com Media 1212 Technical Manual V11 Chapter 6compressed Pdf
Celotex GA 4000 Floor Installation Guide As upper mentioned, Celotex GA 4000 insulation boards can have a number of different application, why they can be successfully installed in concrete slab floors, beam and block floors and suspended timber floors, which will all be discussed right here Concrete slab floorsThis chapter gives guidance on meeting the Technical Requirements for suspended ground floors including those constructed from insitu concrete precast concrete timber joists 521 Compliance 522 Provision of information 523 ContaminantsIn ground floor applications such as concrete slabs and beam and block applications, a VCL is required on the warm side of the insulation This will also help protect the insulation from wet screed or concrete Suspended timber floors are slightly different There are differing opinions around whether to introduce a VCL or not, and where to
So what exactly is a damp proof membrane (DPM) used for?Suspended Timber Floor 1 Install joists in the normal manner, ensuring adequate ventilation 2 Measure gaps between joists and cut Insulation with Perimeter strips DPM 10 gauge Polythene or Radon barrier Beam and block suspended floor Perimeter/Area Ratio (P/A) Thickness (mm) 050 060 070 080 090 If a suspended timber floor is in place, then this can be insulated as shown in our how to video 'How to install Kooltherm K103 Floorboard from above joists in a suspended timber floor' For a solid floor, specific attention should be paid to the construction of the wall, and especially considering if a damp proof course (DPC) is present, as this might not be the case in
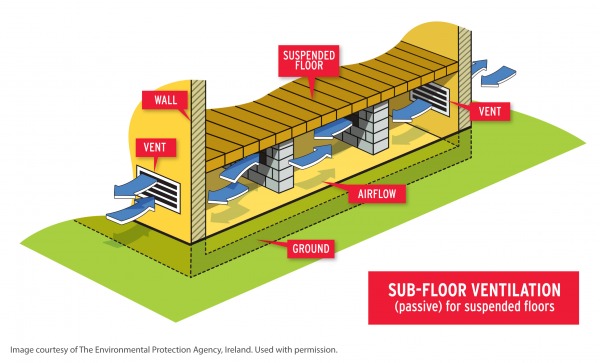
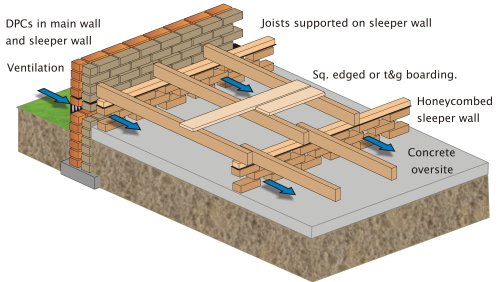
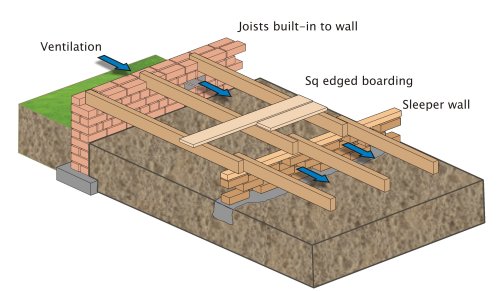
The existing concrete floor can be used as a base, however a new damp proof membrane (DPM) will need to be introduced DPMs come in solid or liquid form, the latter being a practicable solution for a garage conversion Manufacturers will be able to advise A suitable gauge damp proof membrane (DPM) and thermal insulation must be provided43 Suspended concrete or timber groundfloors incorporating the insulation boards must include suitable ventilation of the subfloor void or a dpm 44 When used as insulation in suspended timber groundfloors, for optimum thermal performance, the product shall be installed with the correct orientation of its foilfacing Floors are constructed in two ways, either suspended or solid Suspended timber floors consist of floorboards nailed to joists, often carried on 'sleeper' walls of brick It is important that the underside of a suspended floor is ventilated to avoid the build up of moisture



New Floorboards Dpm Insulation Questions Diynot Forums



Evolution Of Building Elements
Method 1 Damp proof membrane (DPM) • A DPM should be provided beneath the screed or insulation;If appropriate, lay a damp proof membrane (DPM) (normally 10g polythene sheet/300g micron), to the top surface of the beam and block floor Level the surface of the floor;A damp proof course (DPC) should be placed between the timber and the wall Insulation is then placed between the joists (thickness depends on the product used) Air vents should be placed underneath to provide ventilation to the void and the air should be able to travel from one side of the building to the other Suspended concrete floor




Detail Post Floor Details First In Architecture




Building Standards Technical Handbook 17 Non Domestic Buildings Gov Scot
• Radon barrier/DPM & DPC • Insulation • Sub floor Main Floor Types Suspended Timber Floor Above is a sketch of a Suspended Timber Floor The main materials used in the type of floor is Concrete and Timber Since timber is being used, rot can become a major issue Hi It is ok to put a DPM/membrane on the floor and the the Celotex on top Years ago you could get away with timber battens to fix the floor to but not Post a job Homeowners Post a job How it works About us Suspended timber floor insulation / underfloor heating Insulating suspended timber floors vapour barrier or no vapour barrier?



A Best Practice Approach To Insulating Suspended Timber Floors Ecological Building Systems




Timber Frame Construction And Insulation Sitework Ballytherm Co Ukballytherm Co Uk
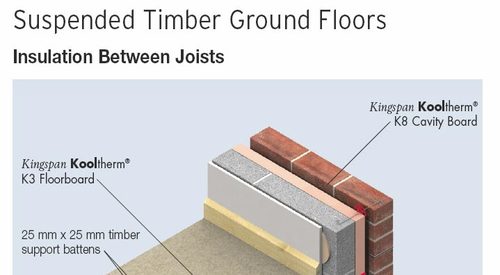
Materials For Suspended Timber Floor Insulation There are three main options Celotex / Kingspan type PIR thermal insulation board This comes in various thickness (50mm and 100mm are the most common) and in a variety of sizes (24 x 12m being the most common)NHBC requires ground floors to be constructed as suspended floors in the following situations where the depth of fill exceeds 600mm, as described in Chapter 51 'Substructure and ground bearing floors' (Design) where soil swelling may occur, as described in Chapter 42 'Building near trees' on sites which have been subject to vibratory groundFloor Insulation Systems are used below the floor slab, lay the hardcore in layers (min mm) Each layer should be wellcompacted with the surface blinded with quarry dust or sand to provide a suitable surface for laying a DPM (damp proof membrane) A DPM, eg 10 gauge polythene, or a radon



Building Guidelines Concrete Floors Slabs



Spray Foam Insulation Concrete Slab Floor
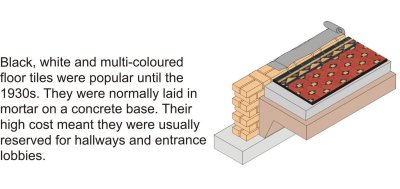
The flexible nature of mineral wool accommodates movements in floor ensuring all joints remain closed Note The Uvalues have been calculated assuming that the timber joists are 48mm wide at 600mm centres with a default fraction for the timber floor of 011 taken from BR443 Floor covering assumed as 18mm chipboardThis is how the renovation all started so at least we had a tried and tested method to use We had intended to Traditional ground floors have consisted of little more than a few flagstones or bricks placed directly over the soil The Victorian era saw the widespread introduction in mass housing with suspended timber floors, alongside rudimentary solid floors in hardwearing areas such as kitchens and hallways This combination persisted well into the 1930s, with solid concrete




Removing Insulating And Restoring A Suspended Wooden Floor Part 2 Of 3 Youtube




Should You Replace Your Old Timber Floor With A Concrete Floor Dampchat
Insulating Above Precast Concrete Floors – Design Guidance Suspended floors do not require a DPM If a radon barrier is required, it can be put in on top of the structural surface beneath the insulation, or within the subfloor void's concrete covering All radon barriers must reach across the whole footprint of the buildingTECHNICAL DATA SHEET FLOOR INSULATION –SUSPENDED TIMBER FLOOR Jabfloor 70 Dampproof membrane A suitable DPM such as 10 gauge polythene must be installed in the floor either above or below the concrete slab, (See diagrams) If a liquid DPM is used, care should be taken that it is compatible with Jabfloor, and that it is In this way suspended timber floors insulation will ensure proper heating and cooling in the home It also guarantees quality, reduced carbon foot print, cost effectiveness and easy installation Cost of suspended floor insulation Professional suspended floor installation costs range between £30 t0 £40




Finishing To Threshold Over Cavity Timber Floor Page 1 Homes Gardens And Diy Pistonheads Uk




Building Standards Technical Handbook 17 Non Domestic Buildings Gov Scot
It applies to suspended timber floors located above an unheated space, where the insulation is installed below the floorboards or timber decking timber floors situated above an unheated integral although i dont like concrete floors, in your case a slab floor will possibly be a lot cheaper than a suspended floor but price will depend on a number of factors you will need a min of 150mm space below your suspended floor joists, & venting or air bricks at the rear elevation you will also need a min of three air bricks at the front elevatonCurrently building a SIPS house on a beam an block floor Beam and block floor will be topped with DPM 100mm Celotex second thinner dpm 65mm screed with UFH wood floor SIPS design drawings show the outer SIPS walls sitting directly on a sole plate on the beam / block floor (



Technical Hub Insulation Boards Kingspan Ireland



Www Scoilnet Ie Uploads Resources Pdf
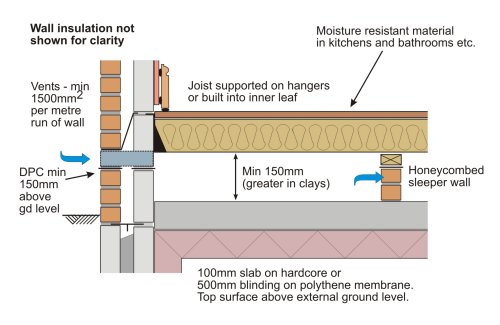
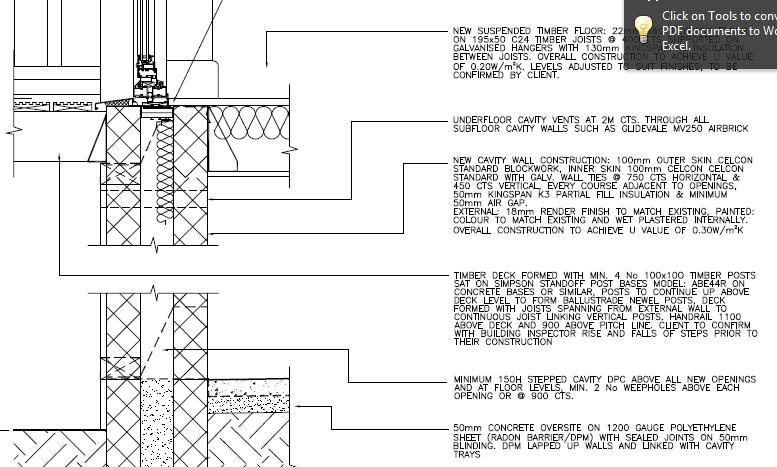
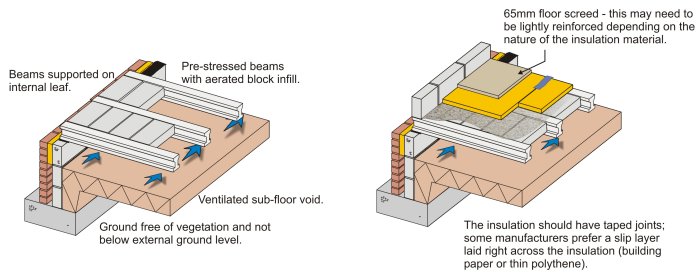
Ventilation and Cavity tray, insulation between joists, joist hangers, Chipboard floor finish, hardcore subbase / DPM abd concrete slab (mm)The floor void beneath the beams should be appropriately vented, ensuring that a cross flow of air between two external walls is achieved • The minimum area of ventilation should equate to at least 1500mm2 per metre run of external wallMy kitchen floor is made up of half suspended timber and half solid concrete I have the following 2 questions need 150mm of consolidated clean compacted hardcore then a sand blinding followed by DPM 150mm of concrete another DPM then soild insulation around mm Finished off with a screed, 75mm




Ground Floors Wall Concrete



Suggestions On Insulation Of Solid Floor
A damp proof membrane can be installed over the top and then, along with a levelling layer, a 22mm wood fibre insulation board and Lithotherm underfloor heating tiles, the floor finish can be laid If you'd like advice on how to insulate your suspended floors please contact us at chris@backtoearthcouk or alternatively give us a call onDPM, Slab, Insulation, Vapour Barrier, Underfloor Heating Loops, Floor Screed Suspended timber floor constructions The nature of suspended timber floors means they are, inevitably, more prone to movement than screed This said, much can be done to minimise movement and allow successful use of tiles Well fitted joists are extremely strongEffectively, a damp proof membrane (DPM) is used to create a barrier between a concrete (or screed) subfloor and a wood floor This barrier is intended to stop moisture passing from one to the other




Garden Room Workshop Part 6 Insulation Plywood Floor Youtube




Underfloor Thermal Insulation Of Suspended Timber Floors Craftedforli
41 Celotex TB4000, G000 and XR4000 PIR Insulation Boards for Floor Insulation are suitable for use as floor insulation and are effective in reducing the thermal transmittance (U value) of groundbearing or suspended concrete or timber groundfloors, and also exposed or semiexposed intermediate concrete or timber floors, in new or existingIf the insulation is going below the slab, the damp proof membrane (DPM) is laid next, followed by the insulation, a polythene separating layer, and the concrete slab Depending on the use of the building, the slab can then be finished ready for use, or receive a screed suitable for a floor finishThe floor was vacuumed before applying Aredx DPM IC, an epoxy liquid Damp Proof Membrane (DPM) Grinding the old bitumen from the concrete floor Now the floor is flat the DPM can be applied to seal the concrete Once dry, Arditex NA, a latex based self levelling compound, was applied A water based product would have taken a month to dry, but
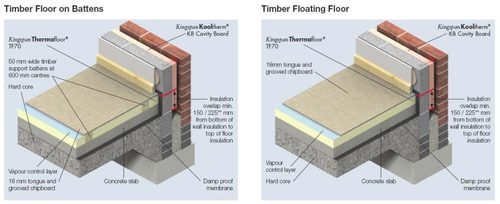



Technical Hub Insulation Boards Kingspan Ireland




Insulating A Timber Joist Suspended Floor Youtube
Timber flooring directly onto the joists, fixing in the normal manner Ensure that the void below the insulated suspended floor is well ventilated and that sleeper walls do not restrict the airflow Cutting Onsite trimming of boards where necessary to maintain continuity of insulation around opes is easily executed using a fine tooth saw orXT/UF Beam & Block Suspended Floor 65mm Screed Separating layer polythene sheet Insulation with perimeter strips DPM 10 gauge polythene or radon barrier beam and block suspended floor Buildup 0 030 040 050 060 070 080 090 100 Target UValue Thickness (mm) 30 45 50 55 60 60 60 65 65 025 Thickness (mm)43 Suspended concrete or timber groundfloors incorporating the insulation boards must include suitable ventilation of the subfloor void or a dpm 44 When used as insulation in suspended timber groundfloors, for optimum thermal performance, boards with printed foilfacings shall be installed with the correct orientation




Cpd 10 18 Flooring Insulation Features Building Design



Www Kore System Com Wp Content Uploads 19 01 Kore Floor Iab Certificate 19 Pdf
Well over 5 years later and I am back at it! Timber Floors Although timber ground floor construction used to be a popular method, today it is not as common as the concrete alternatives A suspended timber floor is constructed as a timber platform of boards nailed across timber joists supported on sleeper walls, and the external and internal load bearing walls surrounding them You need a fair bit of thickness for a new solid floor 150mm type 1, bit of sand blinding, DPM, 100 concrete slab, 70mm celetex (nb to building regs requirement so could be more), 70mm screed = 290mm reduced dig measured from underside of floor finish Mind you suspended is probably 50mm slab, 150mm void, 150mm joist




Garden Room Workshop Part 5 Timber Floor Youtube



Suggestions On Insulation Of Solid Floor
These can be classed as either Suspended or Solid Solid floors are a lot more substantial and require the ground to be made up in layers of ground sub base, sand, compacted hard core, damp proof membrane, insulation and concreteIt should be smooth and free of projections Use a thin layer of sandblinding to ensure that the insulation boards are continuously supported if requiredLaying between the joists of a suspended timber floor KORE Floor Insulation System should be cut to fit between the timber joists and supported by carriers These may be nails partdriven into the side of the joists at selected level, timber battens or proprietary saddle clips Where services need to be accommodated below
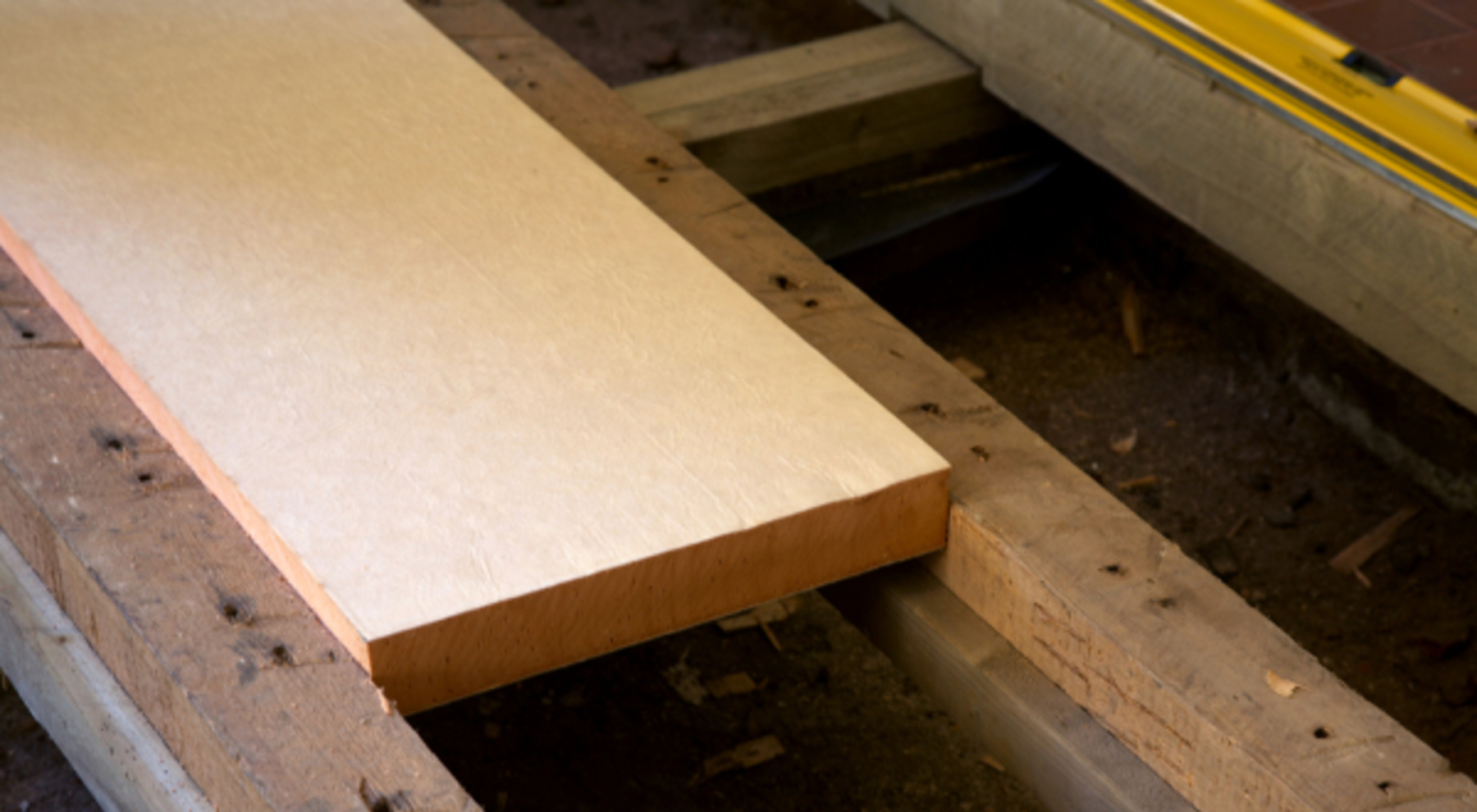




Insulating Under A Suspended Timber Floor Insulation Kingspan Great Britain




Detail Post Floor Details First In Architecture
Started by dave_dsbluesfsnetcouk , 621 PM I'm about to insulate under the drafty suspended timber floor of my 1908 house using either celotex (or similar) or possibly sheeps wool battons pushed up between the joists (and also various tapes, foam etc to



Http Www Sparaochbevara Se Wp Site Content Uploads 18 02 Casestudy11 Ndmh 01 18 Pdf




Core 05 Floor Construction Diagram Quizlet



Www Premierguarantee Com Media 1212 Technical Manual V11 Chapter 6compressed Pdf




What Can I Do About A House With Internal Concrete Floor With No Dpm Home Improvement Stack Exchange




Floor Insulation How To Make Your Home Warmer By Insulating Old Floors Real Homes




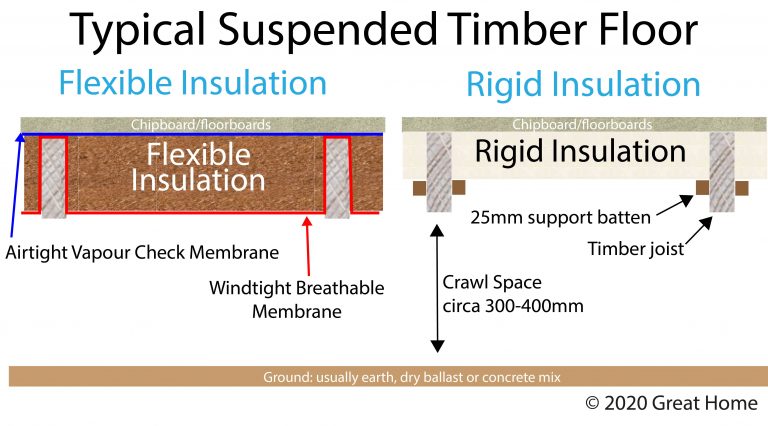
Underfloor Insulation Of Suspended Timber Floors Great Home



Www Premierguarantee Com Media 1212 Technical Manual V11 Chapter 6compressed Pdf




How To Replace A Timber Floor With Concrete Sully Road
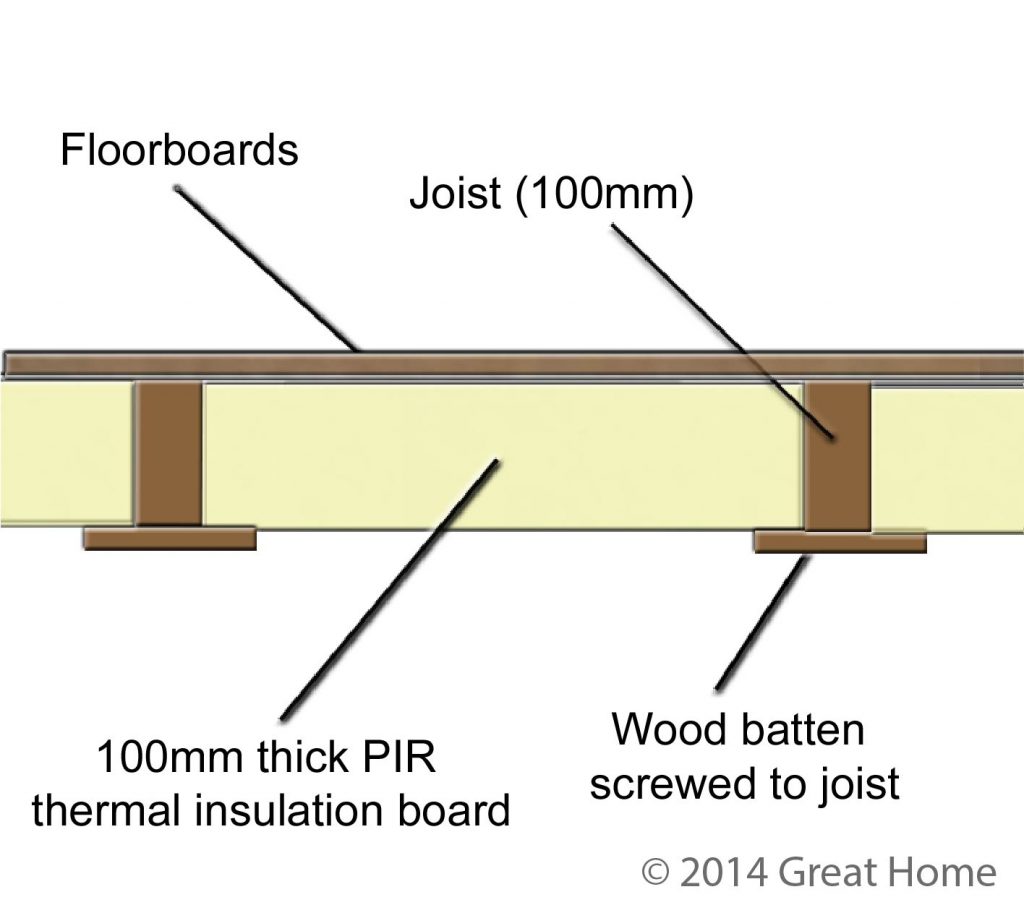



Underfloor Insulation Of Suspended Timber Floors Great Home




Suspended Timber Floor By Bpptech Issuu




Insulating Above Precast Concrete Floors Design Guidanceballytherm Co Uk
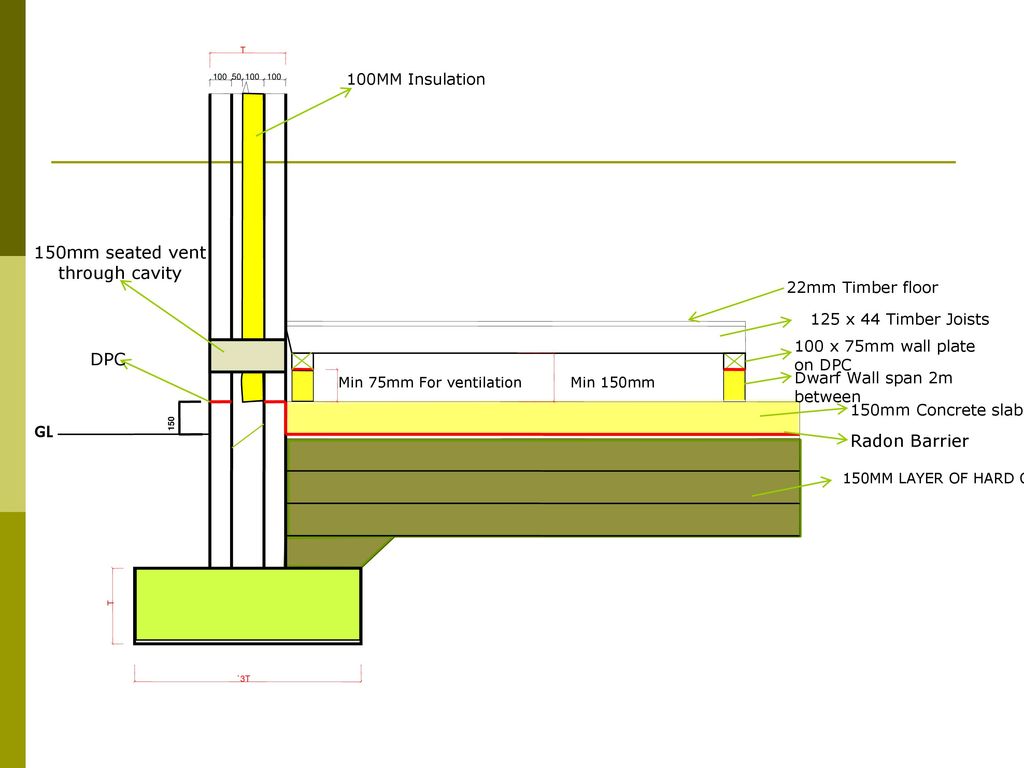



Concrete And Suspended Timber Ppt Download
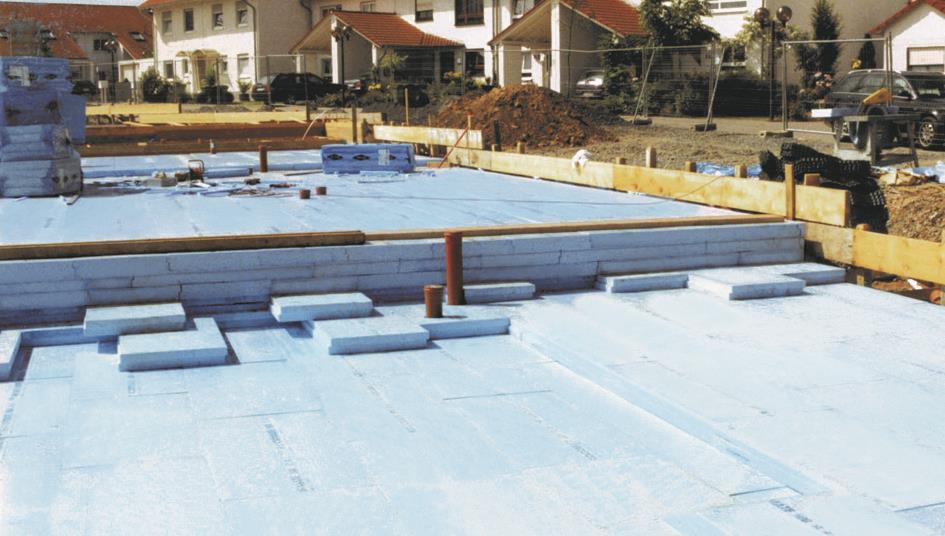




Cpd 10 18 Flooring Insulation Features Building Design



The Best Ways To Insulate Your Floor




Suspended Beam And Block Floor Quinn Building Products Floor Insulation Insulation Insulation Thickness



Www Premierguarantee Com Media 1212 Technical Manual V11 Chapter 6compressed Pdf
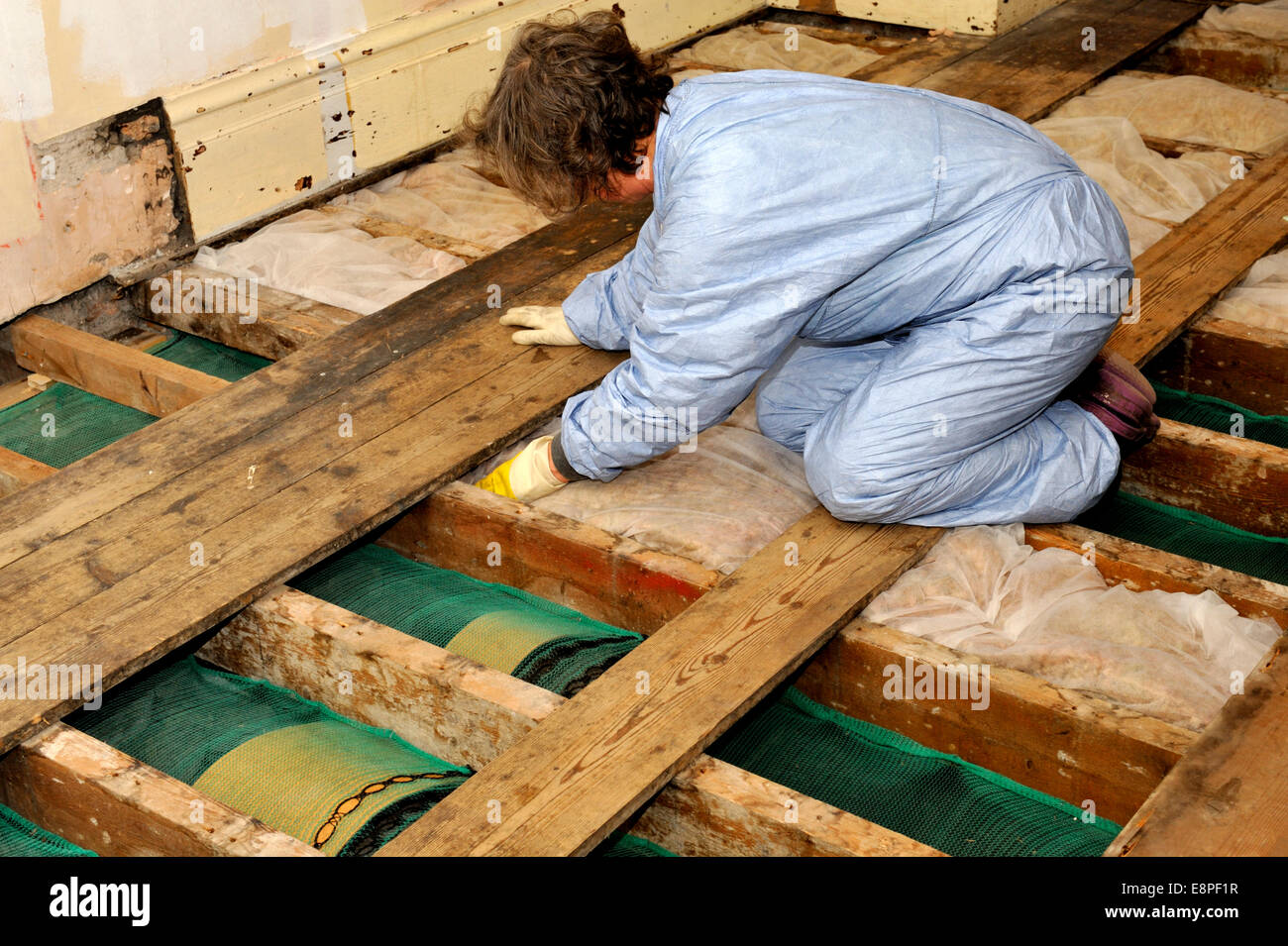




Floor Insulation High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Passive House Floor Insulation Passive House House Flooring Floor Insulation
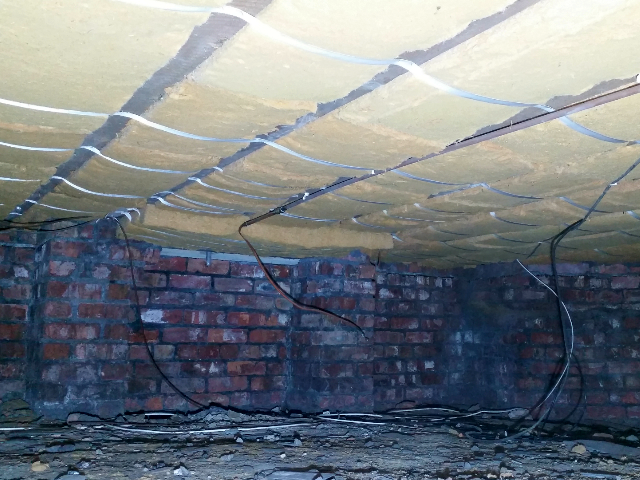




Suspended Timber Floors Red
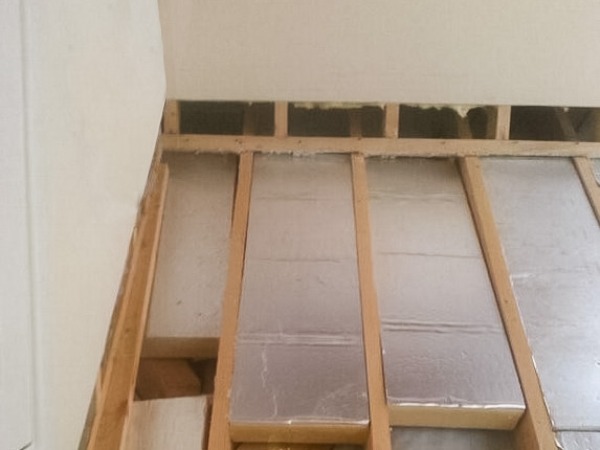




A Best Practice Approach To Insulating Suspended Timber Floors Ecological Building Systems



Building Guidelines Concrete Floors Slabs
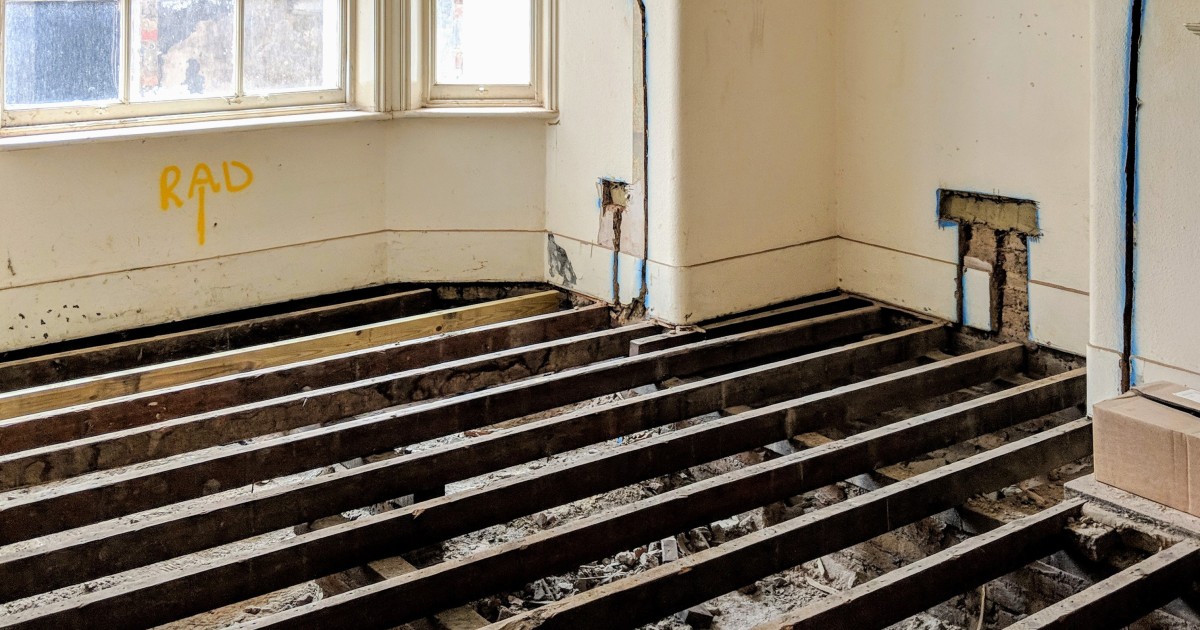




A Best Practice Approach To Insulating Suspended Timber Floors Ecological Building Systems




Insulation Below A Groundbearing Slab Sitework Ballytherm Co Ukballytherm Co Uk



Www Scoilnet Ie Uploads Resources Pdf




Fbe 03 Building Construction Science Lecture 3 Floor



Q Tbn And9gcsoo00pmp Jo39lntwqiman Kyqnkiizr2egma 29un93tjzu39 Usqp Cau




Concrete Vs Timber Floors



Replacing My Suspended Floor With An Insulated Floating Floor
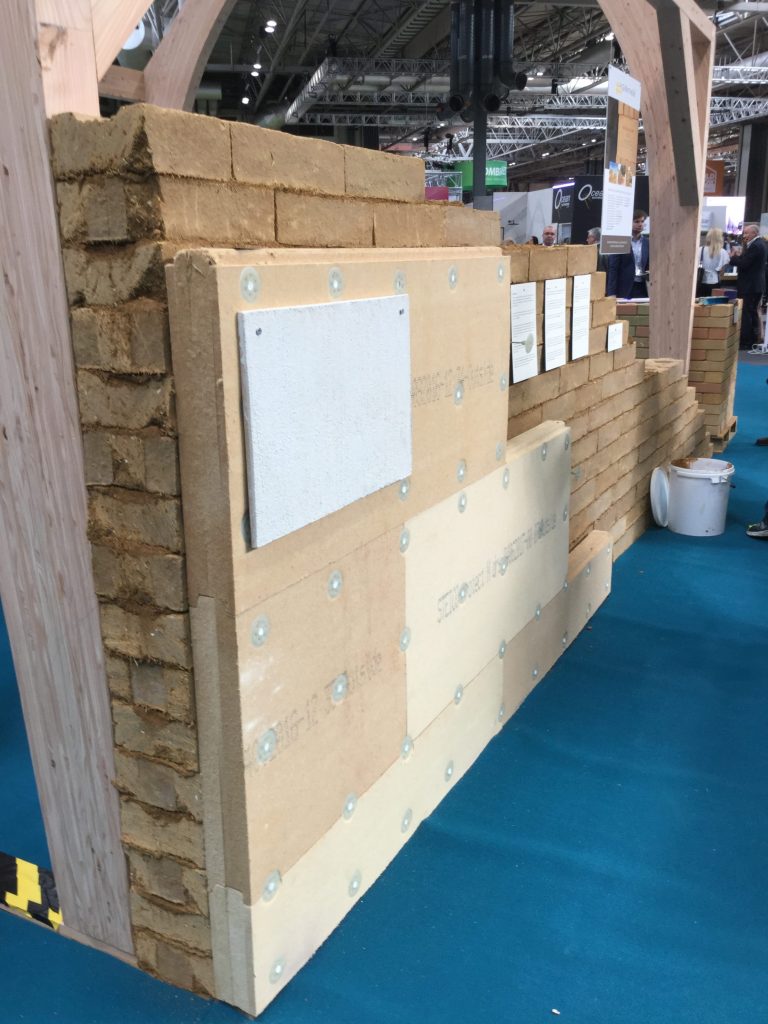




Gbe Insulation Properties Materials Green Building Encyclopaedia
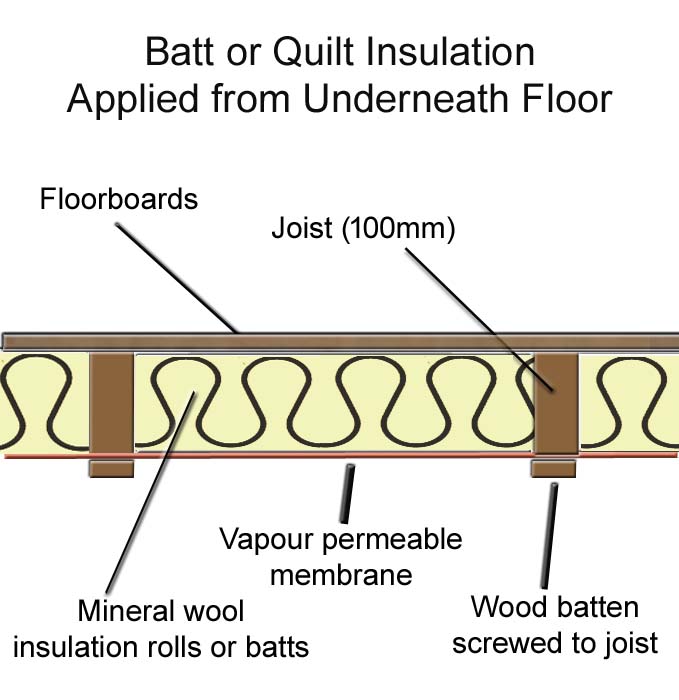



Underfloor Insulation Of Suspended Timber Floors Great Home




Adding Underfloor Insulation To Existing And Older Properties



Evolution Of Building Elements



Replacing My Suspended Floor With An Insulated Floating Floor



1




Greenspec Housing Retrofit Ground Floor Insulation



Evolution Of Building Elements



Dpc In Cavity Wall Diynot Forums



Underfloor Insulation Of Suspended Timber Floors Great Home




Floors Construction After The Foundations Have Been Completed And The External Walls Constructed The Construction Of The Floors Commences Ppt Download



Convert To Solid Floor



Replacing Suspended Timber Floor




Ask The Expert Thermally Upgrading Suspended Floors Ecological Building Systems




Finishing To Threshold Over Cavity Timber Floor Page 1 Homes Gardens And Diy Pistonheads Uk
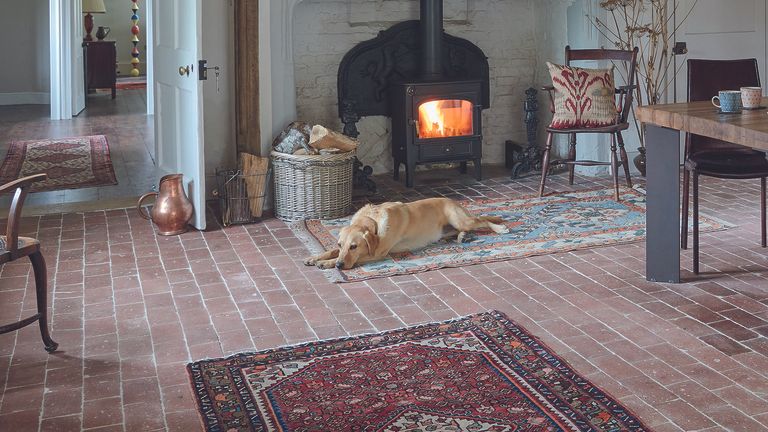




Floor Insulation How To Make Your Home Warmer By Insulating Old Floors Real Homes



Www acerts Co Uk Search Doc 2f1ahz8kxlts3jkx4fa8ec7m 3d




Constructing A Suspended Floor To Building Regs Youtube



Insulating Suspended Timber Floors Green Building Store




Thermal Insulation For Concrete Slab Floors
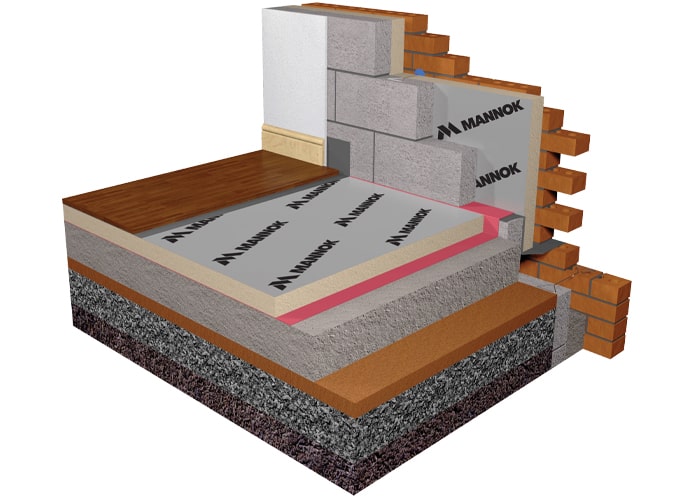



Insulating Solid Ground Floors With A Timber Floating Floor Mannok Insulation




Detail Post Floor Details First In Architecture




What Is A Suspended Timber Floor Discount Flooring Depot Blog



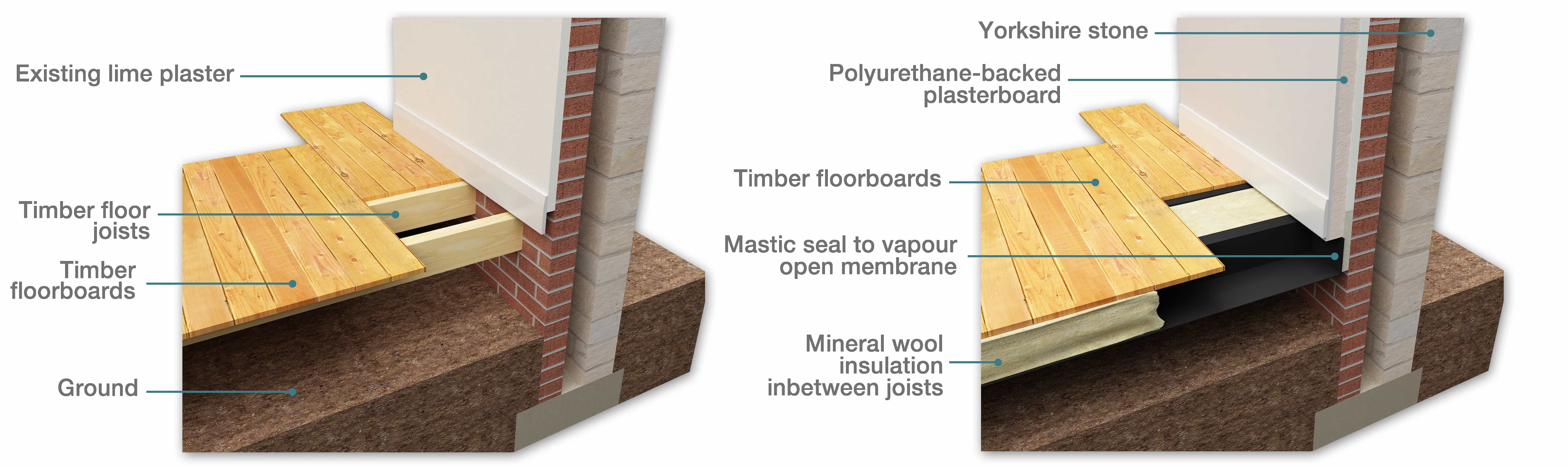
Evolution Of Building Elements
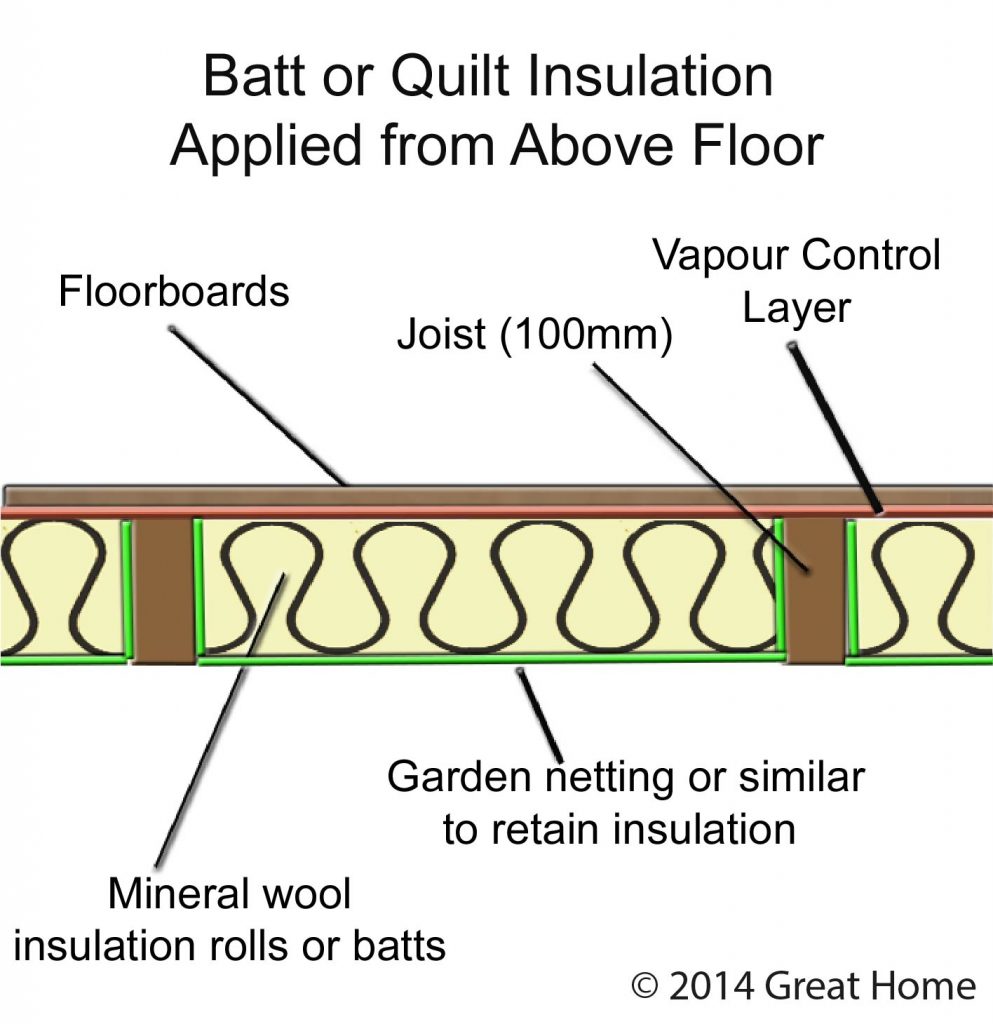



Underfloor Insulation Of Suspended Timber Floors Great Home



1
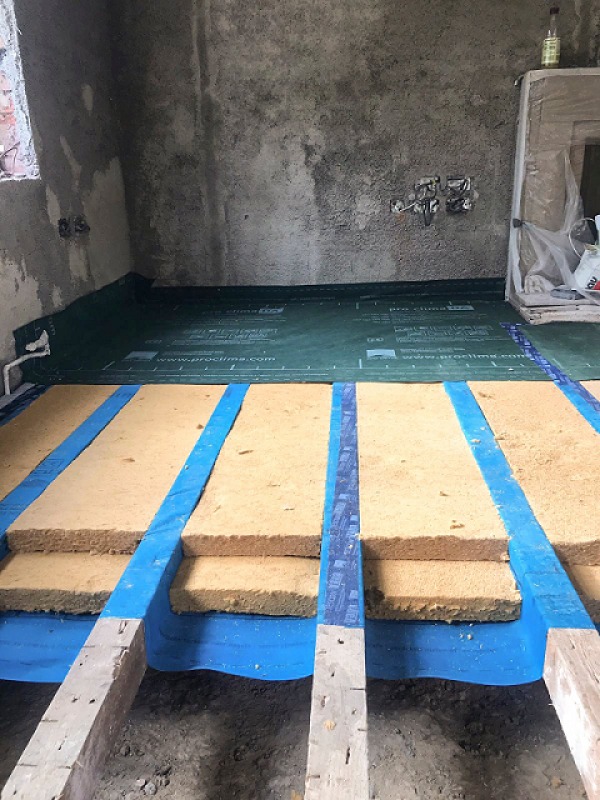




Ask The Expert Thermally Upgrading Suspended Floors Ecological Building Systems




Detail Post Floor Details First In Architecture
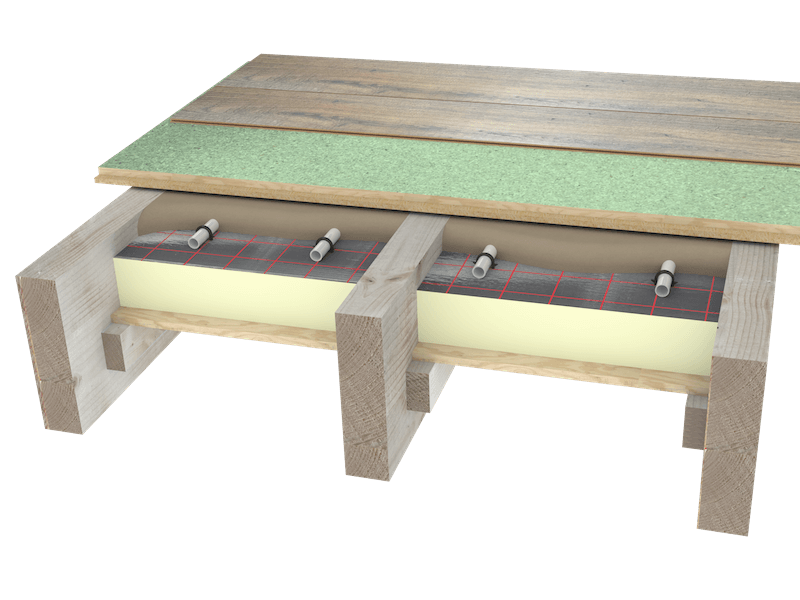



Floor Construction Underfloor Heating Systems Ltd




What Can I Do About A House With Internal Concrete Floor With No Dpm Home Improvement Stack Exchange




Concrete Vs Timber Floors




What Can I Do About A House With Internal Concrete Floor With No Dpm Home Improvement Stack Exchange



Www Scoilnet Ie Uploads Resources 246 Pdf
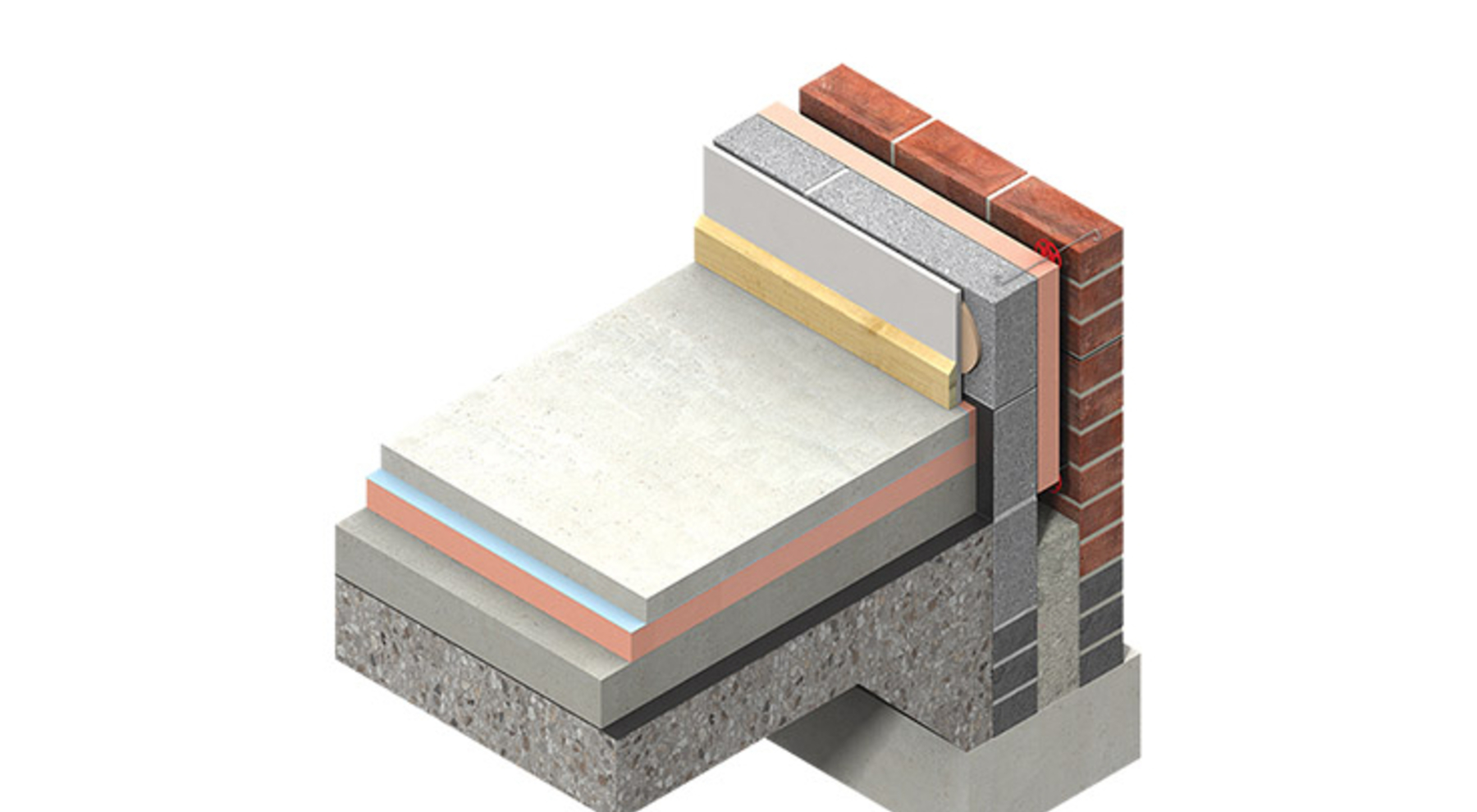



Articles And Advice Insulation Kingspan Great Britain




Suspended Floor Insulation Saint Gobain Insulation Uk




Insulating Above A Groundbearing Slab Sitework Ballytherm Co Ukballytherm Co Uk
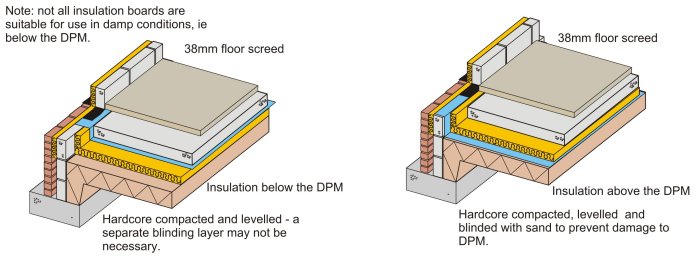



Evolution Of Building Elements




Introduction To Beam And Block Floors Construction Detailing And Selection




Floor Insulation Kore Nzeb Floor Insulation Kore Insulation




Ground Floors Concrete And Suspended Timber Types Of



Insulation Under Timber Floor



1



Conflicting Advice Over Suspended Timber Floor Can Anyone Help Diynot Forums




Underfloor Thermal Insulation Of Suspended Timber Floors Craftedforli
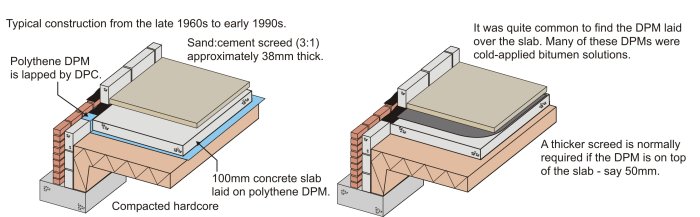



Evolution Of Building Elements




Insulating A Floor Insulation Superstore Help Advice



Www Scoilnet Ie Uploads Resources 246 Pdf



Evolution Of Building Elements




Building Standards Technical Handbook 17 Non Domestic Buildings Gov Scot



Www Jablite Co Uk Wp Content Uploads 16 12 Jabfloor Insulation Suspended Timber Floor Pdf


